JAVA INHERITANCE
inheritance in java
Why use inheritance in java
- For Method Overriding(so runtime polymorphism can be achieved).
- For Code Reusability.
- class Subclass-name extends Superclass-name
- {
- //methods and fields
- }
In the terminology of Java, a class which is inherited is called a parent or superclass, and the new class is called child or subclass.
Types of inheritance in java
On the basis of class, there can be three types of inheritance in java: single, multilevel and hierarchical.
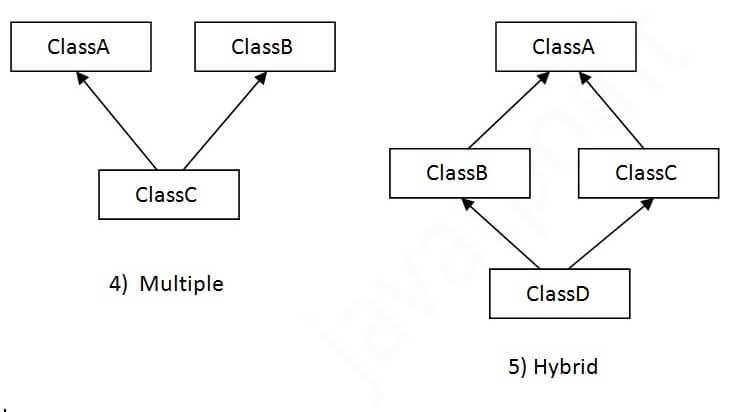
In java programming, multiple and hybrid inheritance is supported through interface only. We will learn about interfaces later.
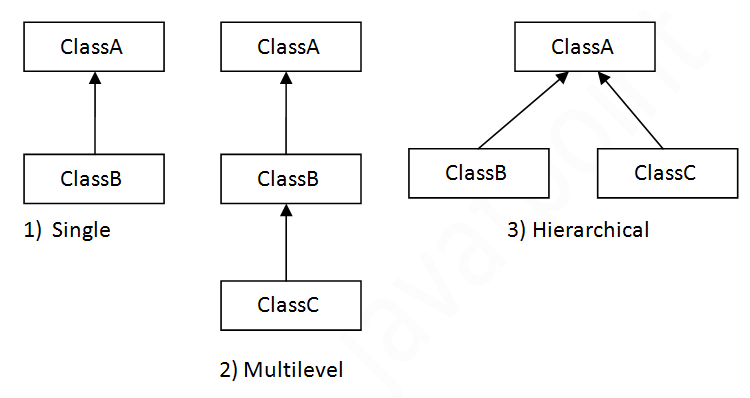
Single Inheritance
When a class inherits another class, it is known as a single inheritance.
Multilevel Inheritance
When there is a chain of inheritance, it is known as multilevel inheritance.
A Java class can't extends more than one class at time , hence Java won't provide support for multiple inheritance with respect to class.
Hierarchical Inheritance
When two or more classes inherits a single class, it is known as hierarchical inheritance
Why multiple inheritance is not supported in java?
To reduce the complexity and simplify the language, multiple inheritance is not supported in java.
Consider a scenario where A, B, and C are three classes. The C class inherits A and B classes. If A and B classes have the same method and you call it from child class object, there will be ambiguity to call the method of A or B class.
Eg
class Animal {
// methods and fields
}
// use of extends keyword
class Dog extends Animal {
// methods and fields of Animal
// methods and fields of Dog
}



Comments
Post a Comment